Platinum temperature sensors are widely used due to their exceptional long-term stability, reliability, high accuracy, ease of use, and reproducible electrical characteristics, defined and standardized as per DIN EN IEC 60751.
Heat meters must have the capability to perform highly accurate temperature measurements year after year to ensure that consumers only pay for the energy they use.
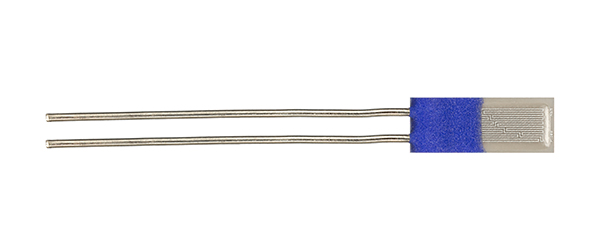
YAGEO Nexensos offers Pt-RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detector) mounted on a small printed circuit board (PCB), designed to meet the strict requirements of heat meter applications. A unique conductive meander located between the SMD (surface mount device) type platinum sensor and the connection pads for the system cable reduces heat transfer and the associated measurement error. This design provides accurate and stable temperature measurement with an immersion depth of only 15mm. The RTD is optimized for assembly in immersion and duct-type sensors, and for operating temperatures from -40 °C to 150 °C. With soldering pads located on opposite sides of the PCB, the need for insulating the solder joint is eliminated. Matching the tube diameter to the sensor width allows for a simple, self-centering, electrically isolated installation, with no need for additional insulation material that might negatively impact response time.
The design optimization minimizes manual assembly steps and supports automated or semiautomated processing. Potting with a thermally conductive paste is recommended for optimal performance.
The small SMD element in a consistent fixed location combined with a minimum required immersion depth significantly reduces thermal mass, resulting in fast, stable measurement over the entire lifetime of the sensor.
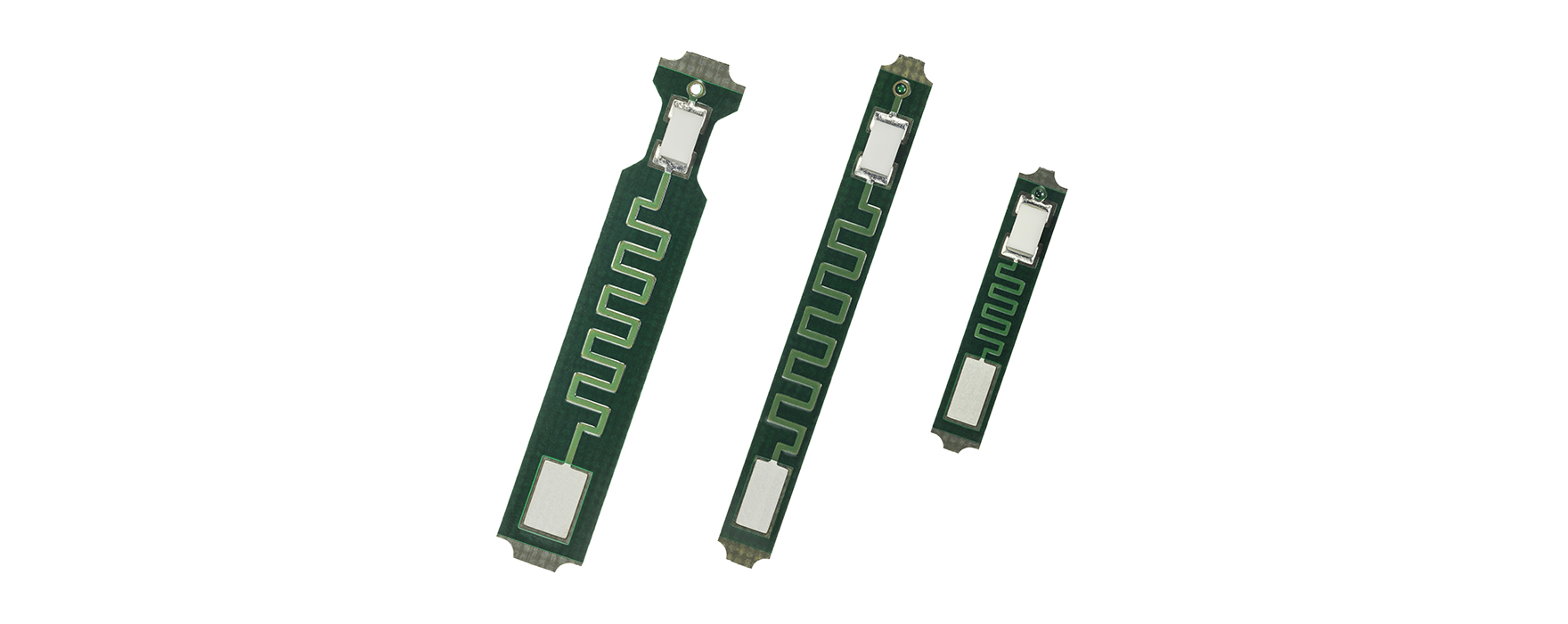

Pt-RTDs on a PCB Also Valuable for Other HVAC Applications

The design features that make the PCB sensor the superior solution for heat meter applications may also improve the performance of other HVAC sensing applications. Air or water temperature measurement reproducibility is dependent upon consistent unit-to-unit sensor location. For example, if the sensor insertion depth varies in a duct temperature measurement application, a measurement variance from installation to installation may occur. The resultant measurement offset could influence setpoint control accuracy. The PCB sensor, with the sensor fixed at a finite, consistent location on a printed circuit board, ensures zero error due to sensor location in a properly assembled sensor probe.